Understanding Basic Probability: From Coin Flapping
Why Probability Matters More Than Students Think
Why do I need to learn this?”—If you’ve ever heard your child complain about basic probability homework, you’re not alone. Many students feel probability is just about flipping coins or rolling dice. Parents worry: Will my child struggle in exams if math feels this abstract?
Basic Probability might sound like a fancy word. But really, it’s just about how likely something is to happen. Whether it’s flipping a coin, predicting the weather, or choosing an exam strategy, understanding real-world chances gives students confidence—and helps parents support them more.
What is Basic Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the occurrence of random or uncertain events. Its value lies between 0 and 1, where 0 means impossibility and 1 means certainty. BYJU’S+2mathsisfun.com+2
Here’s the formula:
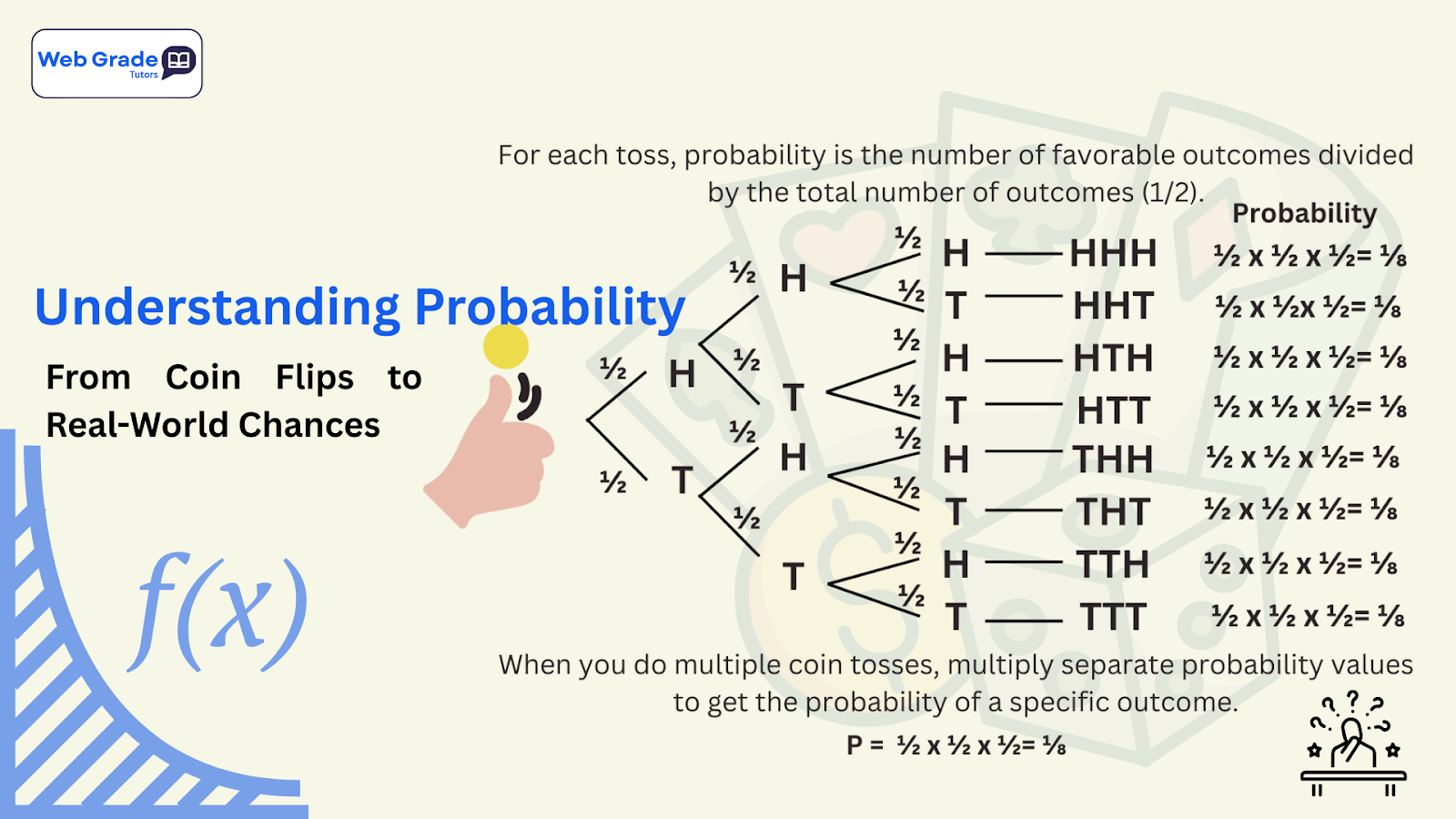
P(E) = (number of favourable outcomes) ÷ (total number of equally likely outcomes)
For example, when flipping a fair coin: the probability of “Heads” = 1 favourable outcome ÷ 2 total outcomes = ½.
In short: Basic probability helps us quantify uncertainty. It’s not about knowing for sure, but understanding how likely something is. That’s very useful in exams and when making decisions—what umbrella to take, whether to gamble, how to interpret forecasts.
Understanding Probability in Simple Terms
Probability is simply the study of likelihood.
Coin flip: Two outcomes → Heads or Tails. Probability = 1 out of 2 = 50%.
Dice roll: Six outcomes. Probability of rolling a 6 = 1 out of 6 (≈ 16.7%).
Everyday life example: A weather forecast of “60% chance of rain” means that in about 6 out of 10 similar days it has rained.
More generally: Probability = (Number of favourable outcomes) ÷ (Total possible outcomes). mathsisfun.com+1
Types of Events & Basic Probability Terms
Here are some important ideas to know:
A certain event
An event that always happens (probability = 1). E.g., the sun is rising tomorrow.
Impossible event
An event that can never happen (probability = 0). E.g., rolling a 7 on a standard six-sided dice.
Likely / Unlikely
Events in between. E.g., chance of rain, chance of drawing an Ace etc.
Complementary events
Two events that cover all possible outcomes.
If A is “Heads”, its complement is “Tails”. P(A) + P(not A) = 1
Rules of Probability You Should Know
Here are some of the basics when working with probability questions:
Basic Probability Addition rule
(for events that don’t overlap)
If A and B are two events that can’t happen at the same time,
P(A or B)=P(A)+P(B)
Example: Probability of rolling a “1” or a “2” on a dice = 1/6 + 1/6 = 2/6 = 1/3.Basic Probability Multiplication rule
(for independent events)
If two events are independent (the outcome of one doesn’t affect the other), then
P(A and B)=P(A)×P(B)
Example: Flipping a coin twice: chance both are Heads = ½ × ½ = ¼.Basic Probability Complement rule
P(not A) = 1 − P(A).
If the chance it rains is 0.7, the chance it doesn’t rain is 0.3.
Real-Life Examples of Probability
Here are some ways probability shows up beyond the classroom:
A weather forecast says: “80% chance of sunshine.” That means it’s been sunny on about 8 out of 10 comparable days. This helps us decide whether to carry a hat, an umbrella, or opt for indoor plans.
Drawing a card from a deck: The chance of drawing a red card = 26 red cards ÷ 52 total = ½.
Rolling two dice: What is the chance both dice show 4? → (1/6) × (1/6) = 1/36.
Medical test accuracy: If a test is “95% accurate, Basic probability helps us understand true positives vs false positives (and why the wording matters).
Probabilities help us plan, strategize, and interpret risk—not just in exams but in choices we make every day.
Why Basic Probability Matters for Exams & Everyday Life
Exam importance: Many school-tests and standardised exams include probability and statistics. If students understand it well, they often perform better in questions about data, risk, percentage, etc.
Decision making: From choosing travel insurance to understanding health risks, probability helps make safer and smarter choices.
Building logical thinking: Learning how to break down problems, use step-by-step reasoning, and avoid misinterpretations.
Probability Exercises You Can Try at Home
Here are three fun and simple exercises—great for students (and parents) to do together:
Exercise 1 (10 minutes): Flip a fair coin 20 times. Count how many Heads, how many Tails. What fraction of flips were Heads? Compare with the theoretical ½.
Exercise 2 (15 minutes): Roll a dice and flip a coin together. Record 30 tries. How many times do you get “Coin = Heads AND Dice = 6”? What was the observed frequency? Compare with the theoretical result: ½ × 1/6 = 1/12.
Exercise 3 (15 minutes): Use a full deck of 52 cards:
Draw one card: What is the basic probability you get a King? What’s the probability you get a red King?
Then draw two cards without replacing: What’s the probability both are Kings?
Formula: (4/52) × (3/51) = 1/221 approximately.
These help students see how theory and real results compare—and remind them that variation is normal.
These help students see how theory matches reality—and when actual results differ, that’s okay. It’s part of learning.
Strategies to Make Probability Easy
Here are three practical strategies to teach or learn probability more effectively:
Start with simple experiments
Hands-on practice beats pure theory: flipping coins, rolling dice, drawing cards. Then compare the experimental results with what the theory predicts.Use stories and games
Make common situations:Predict goals in a football match
Guess the next card in a game
Check whether the weather forecast matched the outcome
Doing this makes “real-world chances” come alive.
Build up gradually
Start with one event (a single coin flip)
Then two events (e.g., coin + dice)
Finally, move into combined word problems that apply to everyday situations and exam questions.
Each step builds in confidence and familiarity.
Quick At-Home Exercises to Try
Exercise 1: Coin & Dice Combo (15 minutes)
Flip a coin and roll a dice together.
- Question: What’s the chance of getting Heads + a 6?
- Answer: ½ × 1/6 = 1/12.
Try it 24 times and compare your child’s results with the theory.
Exercise 2: Weather Forecast Game (10 minutes)
Check tomorrow’s weather forecast.
- Prediction: 40% chance of rain.
- Ask your child: “Out of 10 days, how many should be rainy?”
- Track results for the week. This makes probability real and fun.
Exercise 3: Card Deck Challenge (15 minutes)
Pick a card at random from a 52-card deck.
- What’s the chance it’s red? (26/52 = ½).
- What’s the chance it’s an Ace? (4/52 = 1/13).
- Extra: Pick two cards without replacing. What’s the chance both are Aces? (4/52 × 3/51 = 1/221).
How Tutoring Helps You Master Probability
WebGrade Tutors know how to work; here’s how tutoring makes a difference.
Explains basic probability step by step: using simple words, real-life examples, and visuals.
Addresses where students get stuck: maybe the concept of “independent events” is fuzzy, or maybe mixing up “and/or.”
Practice with feedback: Immediate correction when there’s misunderstanding.
Builds confidence: Each solved example helps reduce anxiety about probability in exams.
Common Mistakes Students Make
It’s normal for students to get tripped up. Here are some classic mistakes:
Thinking past results changes future ones
Example: After flipping 5 heads in a row, many students believe a tail is “due.” But each coin flip is independent. The chance of heads is always 50%, no matter what happened before.
Expecting perfect balance
Students think that in 10 flips, you must get 5 heads and 5 tails. In reality, you might get 7 heads and 3 tails. Over time, though, results average closer to 50/50.
Mixing up “zero probability” with impossible
Sometimes in basic probability, we say “almost zero chance,” but that doesn’t mean it can’t happen—it just means it’s doubtful.
Understanding these pitfalls helps students feel more in control during exams.
Turning Confusion Into Confidence
Probability doesn’t have to be scary. With clear explanations, real-world examples, and a little practice, students can quickly move from “I don’t get it” to “This is easy!”
At WebGrade Tutors, our expert math tutors turn coin flips and dice rolls into real-world understanding. In your FREE 60-minute personalized trial session, your child will:
Grasp basic probability concepts through real-life examples and fun experiments.
Learn exam-ready strategies for data, logic, and problem-solving.
Build confidence and curiosity with interactive, step-by-step guidance.
Conclusion
Understanding basic probability goes far beyond coin flips or dice—it’s a way to make sense of the world. When students see that probability explains how likely things are, it becomes relevant to both exams and daily life.
By learning key rules and event types, they develop logical thinking that helps with decisions—whether predicting weather, analysing results, or planning exam strategies.
For parents and tutors, connecting real-world chances to simple examples like forecasts or games turns abstract math into something meaningful. With a little guided practice, students gain confidence, reduce anxiety, and realise that probability isn’t random—it’s reasoning.
In short, mastering probability improves exam performance and real-life decision-making, transforming confusion into confidence.
Frequently Asked Question?
Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood of events occurring—it assigns a number between 0 (impossible) and 1 (certain) to every event. Understanding probability matters because it helps students make sense of uncertainty—whether in exam questions or everyday decisions.
The basic formula is:
P(E) = (Number of favourable outcomes) ÷ (Total number of equally likely outcomes)
For example, the probability of flipping “Heads” on a fair coin = 1 favourable ÷ 2 possible = ½.
Certain event: happens every time (probability = 1)
Impossible event: cannot happen (probability = 0)
Likely/Unlikely events: somewhere between 0 and 1
Complementary events: two outcomes that cover all possibilities (e.g., Heads/Tails). Their probabilities add up to 1.
Three fundamental rules:
Addition rule (for mutually exclusive events): P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B)
Multiplication rule (for independent events): P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B)
Complement rule: P(not A) = 1 − P(A)
These help students break down complex questions and avoid common errors.
In exams: probability topics show up in data, statistics and risk questions—students who know the rules typically perform better. In real life: probability helps with weather forecasts, insurance decisions, game-strategy, health-risk interpretation and more. When students see the “real-world chances” behind a question, they engage more deeply.
Some common mistakes:
Believing past independent results affect future ones (e.g., “After 5 Heads, a Tail is due”).
Expecting perfect balance (e.g., always exactly 5 Heads in 10 flips).
Confusing “almost zero chance” with “impossible”.
Recognizing these pitfalls builds stronger reasoning and avoids simple traps.
Encourage simple experiments: coin flips, dice rolls or card draws. Compare experimental results with theoretical ones and talk about the difference. Use games and real-life contexts (weather, sports, cards) to make the topic less abstract. Guide students through the rules and give immediate feedback to build confidence.